What is Frequency Domain
Near Infrared Spectroscopy
(fdNIRS)?
In clinical applications, fdNIRS is used to measure optical properties such as absorption and scattering in deep tissue (1-2.5cm). The resulting information can lead to quantitative metabolic measurements of key biomarkers in the tissue such as regional oxygen saturation and hemoglobin concentrations.
Optical Absorption
and Scattering

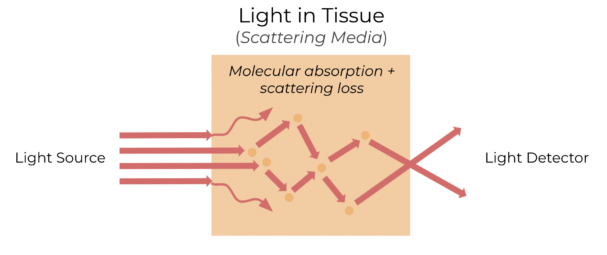
In mediums such as tissue, light is primarily either absorbed or scattered. Scattering increases the complexity of measuring molecular absorption.
Advanced algorithms must then be used on the detected results in order to separate the absorption and scattering data, where an inverse model and known absorption of hemoglobin information are used quantify these 'chromophores' in a tissue volume.
Quantified Metabolic
Information
fdNIRS provides measurements of tissue oxygen saturation, as well as oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin concentrations.
Qualitative oxygenation monitoring.
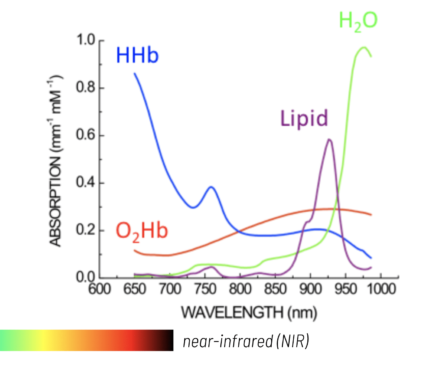
Oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin differ in absorption, and fdNIRS can be used to measure the individual absorption of these biomarkers, providing vital information about tissue health, including oxygenation.
Typical Tissue Absorption Spectra
The NearWave Technique

We modulate 6 laser sources at varying wavelengths and collect the resulting amplitude and phase data.
Eventually, we can develop predictive models to provide clinical diagnostic information.
Technology | Product
Company | Support